The task was to capture and analyze my internet traffic. I used a snippet where I connected to my website”esakontio.com”. I analyzed the connection establishment process. I made the capture at 9:40 on 28.03.2022 by using Wireshark version 3.6.3.
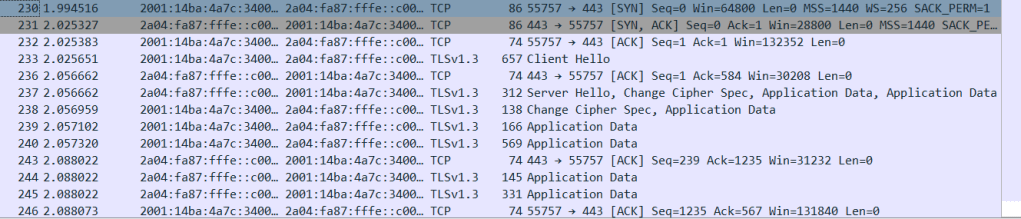
The communication took over IPv6 protocol, as the addresses follow the new format instead of IPv4. First the TCP connection was established. My client sent the connection request SYN in packet 230. The server then responded with a SYN,ACK packet to confirm that the connection request was succesfully recieved in packet 231. My client then answered with the ACK package to acknowledge the answer (packet 232), and the connection was open from both sides.
Then the TLS connection was established in packets between 233 and 238. The used TLS version in this case is the latest 1.3. It could have been determined by the handshake process, which is shorter than in the previous TLS 1.2. The keys are exchanged in the “Hello” packets in TLS 1.3, compared to doing a seperate exchange in the older versions. The connection request for TLS was initiated with the “Client hello” in packet 233. The “Client hello” packet includes data about the client’s TLS version, the client key, a random 32 bit number, session ID and supported cipher suites. The random numbers are used to generate the secret key.
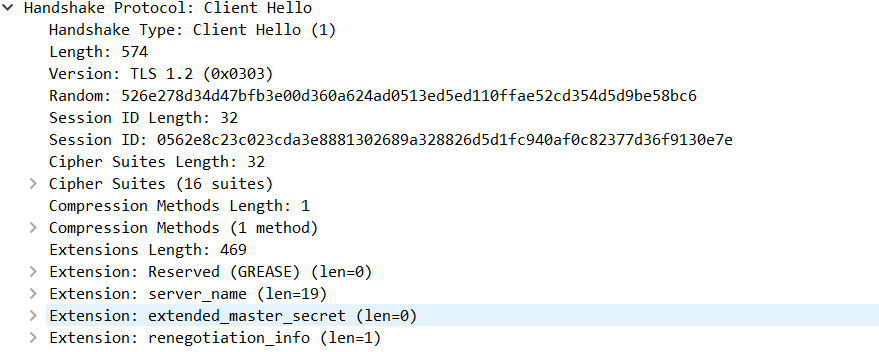
Then the server responded with the standard TCP ACK packet and sent it’s own response after. In the “Server hello” packet, the response included the selected TLS version by the server, certificate, server random (the 32 bit random number), server key, session ID if it was not set by the client and the selected cipher suite from the client provided options.
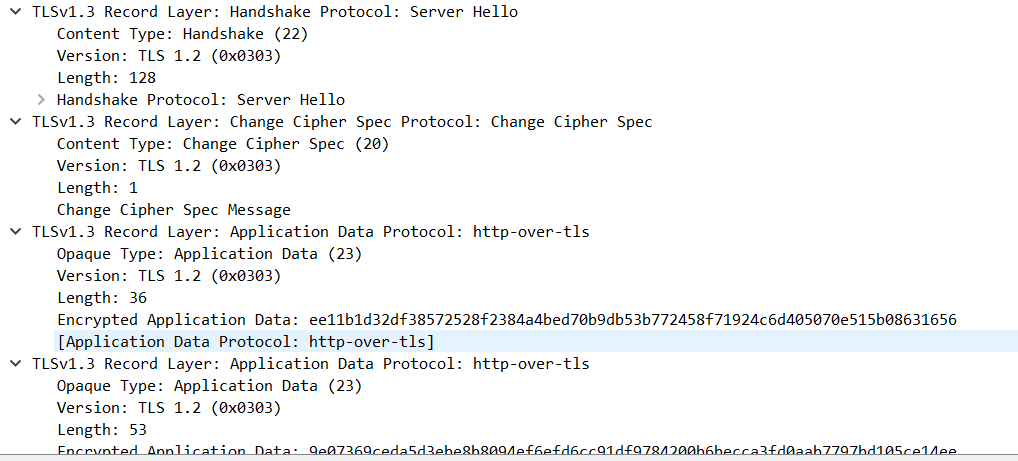
The client checked the certificate and answered accordingly. The certificate was valid. The last step was the client answering with “Change cipher spec” packet, which acts as the acknowledgement for the TLS connection. It can be seen in packet number 238.